I. Introduction
Choosing the right types of roller used in road construction is crucial to project success. With the continuous development of highway construction, increasing vehicle loads, speeds, and traffic volumes place higher demands on subgrade strength and pavement quality. Selecting the appropriate construction road roller based on specific working conditions such as road grade, materials, and pavement thickness is fundamental to achieving high road density, high strength, and smoothness.

This article will help you choose the most suitable road roller equipment for your project from several aspects. First, we will clarify the core functions of the three main types of road rollers; then, we will analyze the key technical configurations and dimensions of road rollers; finally, based on four key factors (project requirements, material properties, project scale, and site conditions), we will provide a practical selection framework to help you make an informed decision.
II. Different types of road rollers used in road construction
The fundamental differences between the three main types of construction road roller lie in their compaction principles and effects, which directly dictate their application scenarios. In many road construction projects, they are used in a complementary sequence to achieve a perfect finish.
1. Single Drum Roller: The “Deep Compaction Expert”
Single Road Roller Core Characteristics: Features a single large steel drum at the front and pneumatic tires or a steel drum at the rear. It incorporates strong vibration, providing deep compaction depth and high impact force.
Primary Applications:
Single drum road roller used for compacting the lower layers of a road structure, such as the subgrade and sub-base (e.g., soil-rock mixtures, graded aggregate base courses, fly ash cushion layers).
Single drum road roller is ideal for compacting coarse-grained, porous materials where deep density is critical (often requiring compaction ≥95%).
2. Double Drum Roller: The “Surface Smoothing Master”
Tandem Road Roller Core Characteristics: Features two steel drums, front and rear. It operates with high frequency and low amplitude vibration, resulting in a smooth, uniform, and level surface.
Primary Applications:
Double drum roller is primarily used for compacting pavement surface layers, especially asphalt concrete during the initial and intermediate (breakdown) compaction stages (e.g., for municipal roads, highway asphalt surface/intermediate layers).Double drum vibrating roller also be used for finishing cement concrete surfaces (in static mode) or for compacting surfaces requiring high smoothness, like pervious or colored asphalt.
3. Pneumatic Tire Roller (PTR Roller): The “Asphalt Kneading Assistant”
Pneumatic Tyre Roller Core Characteristics: Equipped with multiple rows (3-5) of pneumatic tires and a ballast system, but lacks vibration. It relies on the “kneading action” and static pressure of the flexible tires to interlock asphalt aggregate particles.
Primary Applications:
PTR roller is used exclusively for the final compaction (finishing) of asphalt concrete surfaces, particularly effective with modified binders.
Eliminates roller marks left by steel drums, increases surface density, improves skid resistance, and avoids the problem of hot asphalt sticking to steel drums.
The Typical Compaction Sequence:
A standard pavement construction workflow often follows this chain:
Single Drum Roller (for subgrade/sub-base) → Double Drum Roller (for asphalt surface – initial/intermediate compaction) → Pneumatic Tire Roller (for asphalt surface – final compaction).
This sequence ensures deep density, surface smoothness, and final particle interlocking.
III. Technical Considerations for Purchase road roller equipment
When selecting a specific model, in addition to the machine type, it is essential to carefully evaluate the following core configurations and specifications, as they directly affect the equipment’s performance, efficiency, cost, and compliance.
1. Road Roller Engine: The Power Core
The engine is the “heart” of the road roller equipment, and its performance directly impacts equipment reliability.
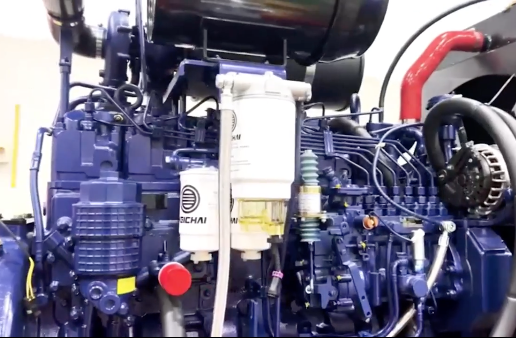
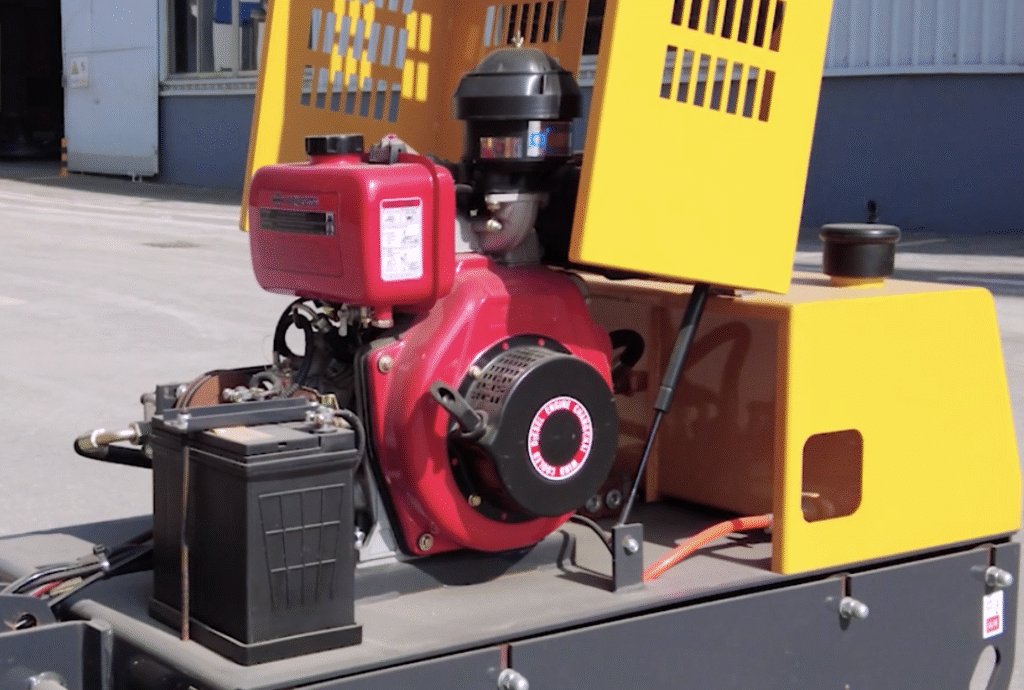

1) Cooling Method:
- Air-Cooled Engine: Simple structure, easy maintenance, low cost. Suitable for small-medium machines or cold regions, but less effective in high-temperature environments.
- Water-Cooled Engine: High cooling efficiency, stable operation, low noise. The preferred choice for modern medium and large rollers, ideal for high-intensity work.
2) Road Roller Engine Major Brands:
- Cummins Engine: A leading global US brand. Renowned for excellent power, fuel economy, and high reliability, especially leading in high-pressure common rail technology. Widely used in high-end and large rollers of various brands.
Weichai Engine: One of China’s largest and most comprehensive engine manufacturers. Known for strong power, large market share, extensive service network, and high cost-effectiveness.
3) Power & Emissions:
- Power: Must be matched to the workload.
- Emission Standards: Must comply with local regulations (e.g., China’s Tier4 standard), a basic requirement for market access.
2. Construction Road Roller Drum Dimensions

Construction road roller drum width determines rolling efficiency while diameter affects obstacle clearance, together forming the foundation of compaction performance.
3. Road Roller equipment Vibration System
The combination of vibration frequency and amplitude defines application scope: high frequency with low amplitude suits surface finishing, while low frequency with high amplitude enables deep soil compaction.

4. Road Roller Tire Configuration
PTR roller utilize specialized tire arrangements and adjustable ballast systems to achieve kneading compaction of asphalt mixtures, ensuring final pavement density and smoothness.
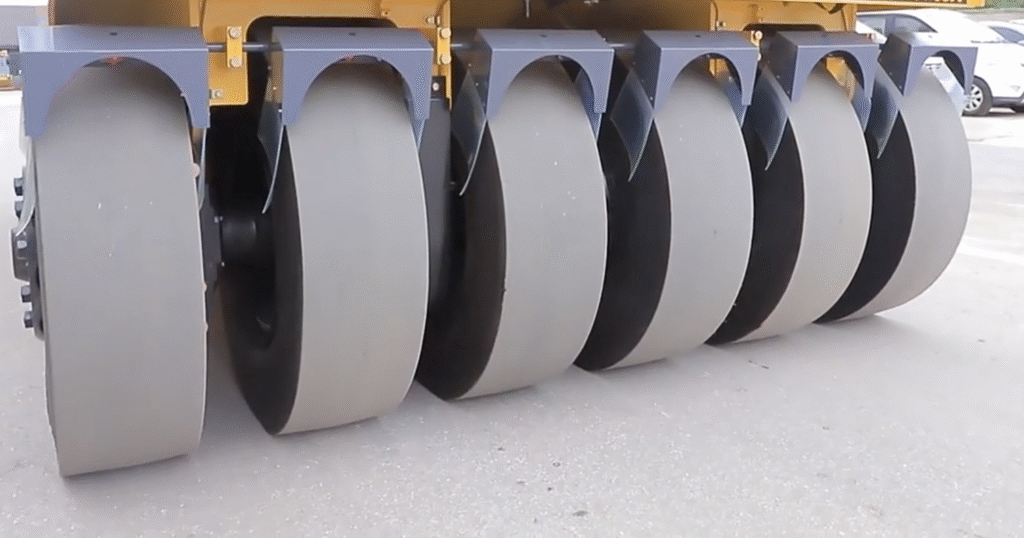

5. Road Roller size – Road Roller Tonnage Selection Guide
The tonnage of a road roller equipment is the most intuitive reflection of its working capacity and is directly related to the scale of the project it suits.
| Tonnage Category | Typical Applications | Key Characteristics |
| Small Road Roller (1-3 tons) | Sidewalks, garden paths, small parking lots, road patching, trench backfilling, bridge abutments. | Highly maneuverable and easy to operate; ideal for small-scale projects, maintenance, and confined spaces. |
| Medium Road Roller (4-10 tons) | Municipal roads, base/surface layers of low-grade highways, building foundation backfilling, general urban construction. | Offers the best balance of power, efficiency, and flexibility; the most versatile and widely used general-purpose model. |
| Heavy Road Roller (12-25+ tons) | Highways, dams, airports, ports, large industrial sites requiring high fill, thick layers, and high compaction standards. | Provides extremely high compaction efficiency and impact energy; essential for achieving deep density on major backbone projects. |
Qhmach is committed to providing a comprehensive product line of road rollers to meet diverse engineering needs. We offer a complete range, from 0.5-ton walk behind rollers to 36-ton heavy-duty rollers, adaptable to various construction scenarios and requirements. Our main products include fully hydraulic single drum rollers, fully hydraulic double drum rollers, and fully hydraulic pneumatic tire rollers (covering 9 wheel roller and 11 wheel roller). Whether for municipal construction, road repair, or large-scale infrastructure projects, Qhmach rollers deliver superior performance and efficient construction, achieving ideal engineering results.
IV. How to Choose the Right construction road roller?
1. Project Quality and Productivity Requirements

The required final quality (density, evenness, strength) and the project’s pace are primary drivers.
- For Uniform Density: Choose a Pneumatic Tire Roller (PTR roller). Its kneading action provides uniform compaction without breaking soil cohesion, ensuring good bonding between layers.
- For Superior Surface Flatness: Opt for an all-wheel drive tandem road roller, which prevents pushing material and improves finish.
- For High Density and Strength: Heavy and Super-Heavy single drum vibratory rollers are necessary to achieve the high density required for strong subgrades.
- Matching Production Rate: The roller’s hourly production volume must match the paver’s laying speed and the plant’s production capacity. This determines the size and number of rollers needed. Using a high-tonnage roller can speed up compaction and shorten the project timeline.
2. Material Type and Layer Thickness

The material you are compacting and its thickness are road roller equipment crucial selection criteria.
| Material / Layer Type | Recommended Road Roller Type | Key Considerations |
| Rock Fill | Heavy Vibratory Roller (Single/Double Drum) | High mass is needed to displace and fracture large rocks. |
| Clay Soils | Padfoot/Sheepsfoot Roller | The pads (feet) penetrate and break the clay’s cohesion. |
| Granular Mixes (Sub-base) | Single Drum Vibratory Roller | Vibration is ideal for settling and mixing different-sized particles. |
| Asphalt Concrete | Double Drum & Pneumatic Tire Rollers | A combination is best for smoothness, density, and sealing. |
| Thin Asphalt Layers (<60mm) | Small Vibratory Roller (2-6t, Amplitude 0.35-0.60mm) | Prevents material shoving, waves, or aggregate crushing. |
| Thick Layers (>100mm) | Large Vibratory Roller (6-10t+, Amplitude up to 1.0mm) | High impact force is needed to achieve density at depth. |
| Deep Layer Compaction | Heavy Vibratory Roller (slow speed, high amplitude) | / |
| Shallow Layer Compaction | Static Roller | / |
3. Select road roller equipment Based on construction conditions and highway type
(1) In areas with a smaller workload and narrower maintenance areas: Small and medium-sized rollers with good steering and maneuverability should be selected.
(2) In areas where it is less likely to cause problems (such as paving layer cracks in asphalt mixtures):Vibratory rollers with high compaction capacity should be selected.
(3) In areas with low compaction requirements: Rollers with lower linear pressure and greater maneuverability should be selected.
(4) For cement concrete pavements: tire-driven tandem vibratory rollers should be selected.
(5) For asphalt concrete pavements: all-purpose vibratory rollers should be selected.
(6) For pavement repair: static smooth-drum rollers should be selected.
4. Job Site Conditions and Space Limitations

Always consider the physical constraints of your worksite.
- Confined Spaces: For trenches, tight corners, or indoor work, choose a roller based on its width and maneuverability. Mini and trench road roller equipment is specifically designed for this.
- Limited Access Areas: If the construction road roller needs to be transported frequently, a smaller, more mobile unit is preferable.
- Sensitive Areas: Where vibration could cause damage (near structures), a static road roller equipment (smooth drum or PTR roller) is required.
V. Conclusion: Choose Construction Road Roller with Purpose
There is no such thing as the “best” road roller equipment, only the most suitable roller for a specific job. By systematically evaluating your project and basing your decisions on four pillars—project requirements, materials and thicknesses, road type, and site conditions—while also considering key technical configurations and tonnage, you can make informed decisions. Choosing the right road roller equipment is a strategic investment that will result in durable, high-quality, efficient, and economical road construction.
If you have any further questions or needs regarding road rollers, please contact us. As a professional road roller manufacturer, Qhmach is committed to providing high-performance road roller solutions. With extensive industry experience and technical support, we can provide tailored advice and services. Whether it’s choosing the right model or technical configuration, we will provide professional consultation to ensure optimal results in every project.



























